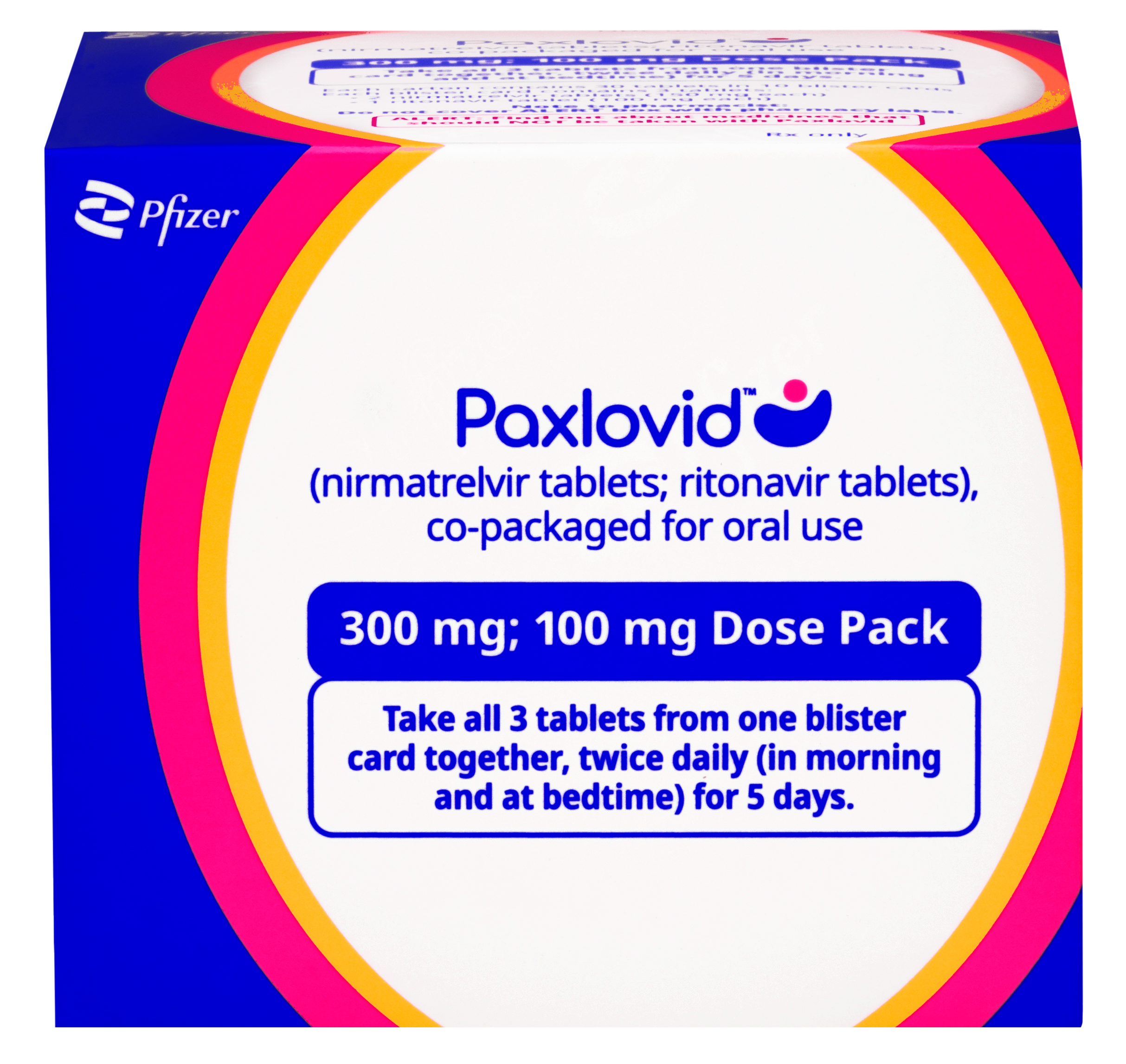
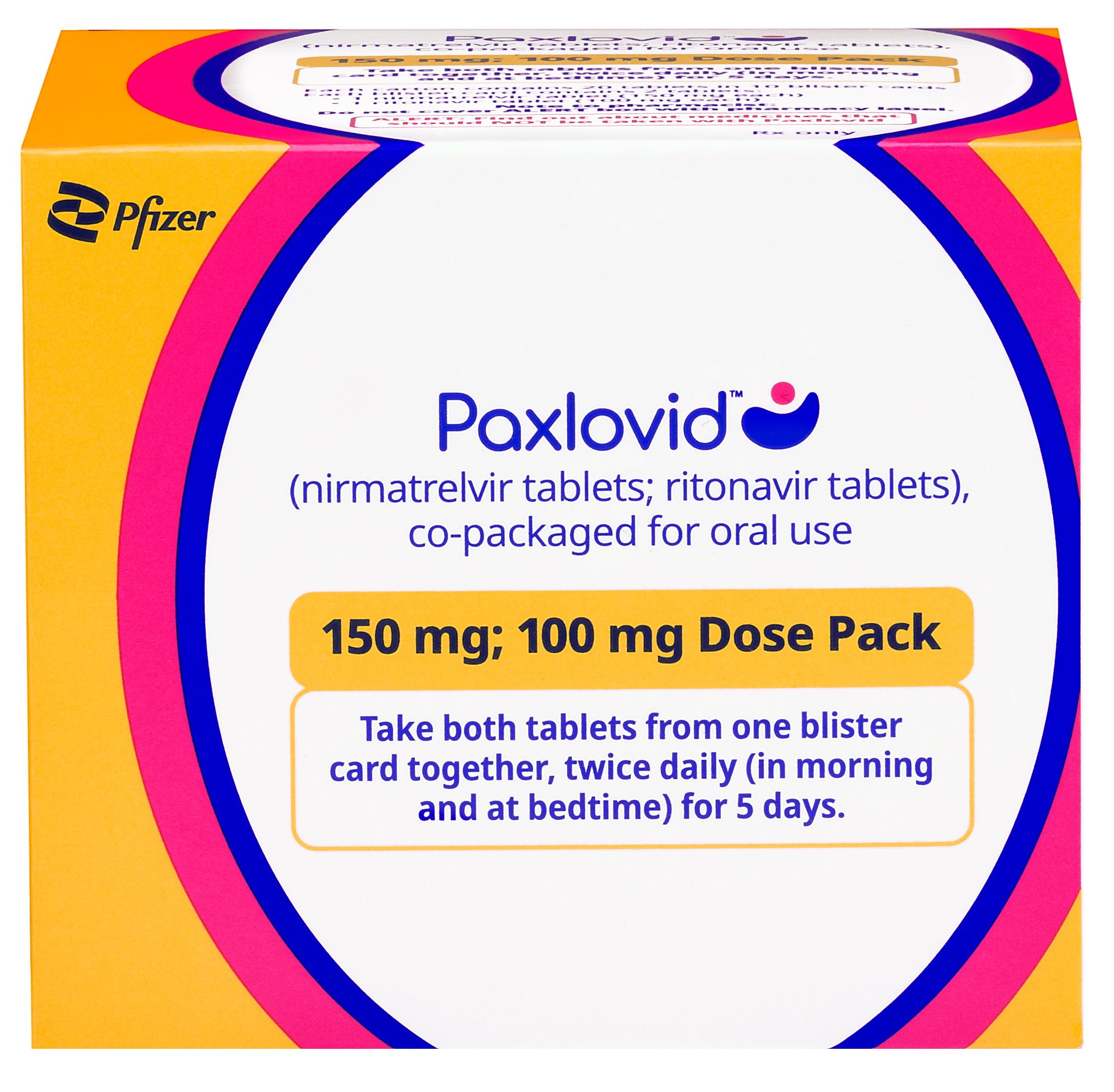
Each box contains 1 or several blister cards with doses of PAXLOVID. Each dose contains 2 types of medicine: nirmatrelvir tablets (pink) and a ritonavir tablet (white to off-white).
There are 3 dose pack options available for PAXLOVID: the standard dose pack, a dose pack for eligible patients with moderate renal impairment, and a dose pack for eligible patients with severe renal impairment. Talk to your healthcare professional to make sure you have the right dose pack.

Learn about what’s inside and on the box.


How to take PAXLOVID
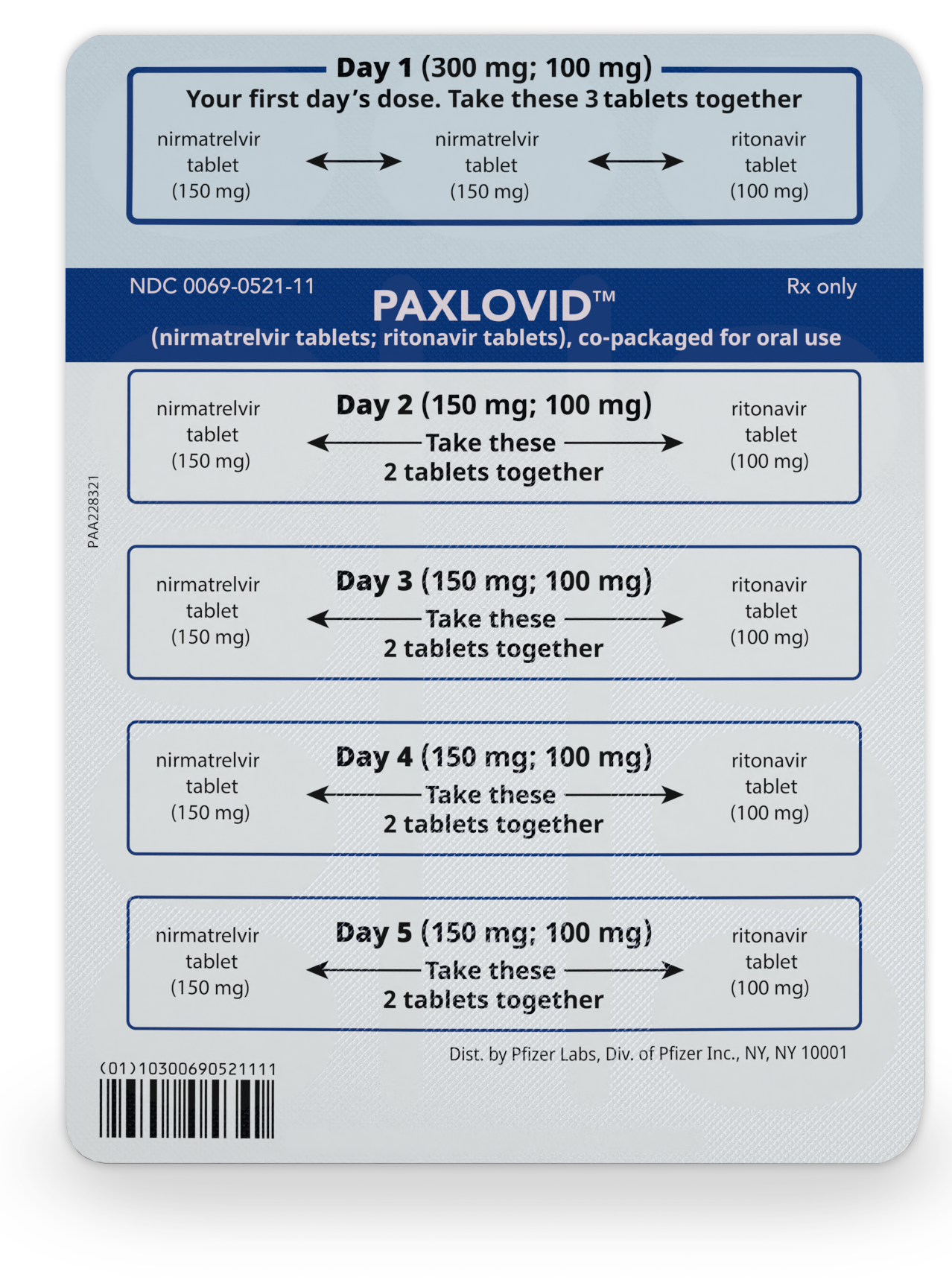
The patient should take the first dose of PAXLOVID in the morning or evening (depending on when the prescription is picked up), or at the time a healthcare professional recommends.
Patients should repeat at the same time each morning and evening until all tablets have been taken.
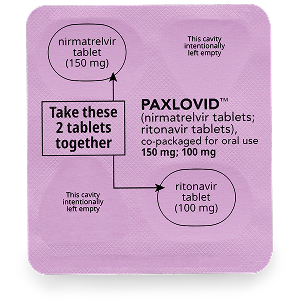
Eligible patients with moderate renal impairment
Patients should take 1 pink tablet of nirmatrelvir with 1 white to off-white tablet of ritonavir by mouth 2 times each day (in the morning and in the evening) for 5 days. For each dose, patients should take both tablets at the same time.
Eligible patients with severe renal impairment
On Day 1, patients should take 2 pink nirmatrelvir tablets and 1 white ritonavir tablet together (blue part of the blister card). On Days 2 to 5, patients should take 1 pink nirmatrelvir tablet and 1 white ritonavir tablet together (pink part of the blister card). PAXLOVID should be taken at the same time each day. On days when patients have hemodialysis, PAXLOVID should be taken after the procedure.

If a dose is missed:
Call a healthcare professional if:
Have more questions about PAXLOVID?
Explore FAQs
Important Safety Information
Significant Drug Interactions. PAXLOVID can interact with other medicines, causing severe or life-threatening side effects or death. Do not take PAXLOVID if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- alfuzosin
- amiodarone
- apalutamide
- carbamazepine
- colchicine
- dihydroergotamine
- dronedarone
- eletriptan
- enzalutamide
- eplerenone
- ergotamine
- finerenone
- flecainide
- flibanserin
- ivabradine
- lomitapide
- lovastatin
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
- lurasidone
- methylergonovine
- midazolam (oral)
- naloxegol
- phenobarbital
- phenytoin
- pimozide
- primidone
- propafenone
- quinidine
- ranolazine
- rifampin
- rifapentine
- St. John’s Wort (hypericum perforatum)
- sildenafil (Revatio®) for pulmonary arterial hypertension
- silodosin
- simvastatin
- tolvaptan
- triazolam
- ubrogepant
- voclosporin
These are not the only medicines that may cause serious or life-threatening side effects if taken with PAXLOVID. PAXLOVID may increase or decrease the levels of other medicines. It is very important to tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements, because additional laboratory tests or changes in the dose of your other medicines may be necessary during treatment with PAXLOVID. Your healthcare professional may also tell you about specific symptoms to watch out for that may indicate that you need to stop or decrease the dose of some of your other medicines. Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare professional.
Before taking PAXLOVID, tell your healthcare professional about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have kidney or liver problems, including hepatitis.
- have Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1) infection. PAXLOVID may lead to some
HIV-1 medicines not working as well in the future. - are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, breastfeeding, or plan to breastfeed. PAXLOVID can pass into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare professional if you are taking combined hormonal contraceptive (birth control). PAXLOVID may affect how your birth control works. People who can become pregnant should use another or an alternative effective form of birth control.
PAXLOVID may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Allergic reactions, including severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis). Do not take PAXLOVID if you are allergic to nirmatrelvir, ritonavir, or any of the ingredients in PAXLOVID. Stop taking PAXLOVID and call your healthcare professional right away if you get any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- skin rash, hives, blisters, or peeling skin
- painful sores or ulcers in the mouth, nose, throat, or genital area
- trouble swallowing or breathing
- swelling of the mouth, lips, tongue, or face
- hoarseness
- throat tightness
-
Liver problems. Tell your healthcare professional right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms of liver problems during treatment with PAXLOVID:
- loss of appetite
- yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes
- dark-colored urine
- pale-colored stools
- itchy skin
- stomach-area (abdominal) pain
The most common side effects of PAXLOVID include: altered sense of taste (such as metallic, bitter taste) and diarrhea.
Other possible side effects include:
- headache
- abdominal pain
- vomiting
- high blood pressure
- nausea
- feeling generally unwell
These are not all of the possible side effects of PAXLOVID. For more information, ask your healthcare professional or pharmacist.
There is limited experience treating pregnant women or breastfeeding mothers with
PAXLOVID. For a mother and unborn baby, the benefit of taking PAXLOVID may be greater
than the risk from the treatment. It is recommended that you use effective barrier
contraception or do not have sexual activity while taking PAXLOVID. If you are pregnant or
breastfeeding, discuss your options and specific situation with your healthcare professional.
Take PAXLOVID exactly as your healthcare professional tells you. If you take too much PAXLOVID, call your healthcare professional or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. If you are taking a ritonavir- or cobicistat-containing medicine to treat hepatitis C or HIV-1 infection, you should continue to take your medicine as prescribed.
Talk to your healthcare professional if you do not feel better or if you feel worse after 5 days.
Contact your healthcare professional if you have any side effects that
bother you or do not
go away.
Report side effects or problems with the appearance or packaging of
PAXLOVID to
FDA MedWatch at
www.fda.gov/medwatch
or call 1-800-FDA-1088
effects to Pfizer Inc. at
www.pfizersafetyreporting.com, by fax at 1-866-635-83371-866-635-8337,
or by
calling 1-800-438-1985
Please see Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers and Fact Sheet for Patients, Parents, and Caregivers.
The FDA has authorized the emergency use of PAXLOVID for the treatment of mild-to-moderate
PAXLOVID is not FDA-approved or available under EUA for use in children younger than 12 years of age or weighing less than 88 pounds (40 kg). There is limited information about the safety and effectiveness of using PAXLOVID in these patients.
Please see Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers and Fact Sheet for Patients, Parents, and Caregivers.
AUTHORIZED USE
The FDA has authorized the emergency use of PAXLOVID for the treatment of mild-to-moderate
PAXLOVID is not FDA-approved or available under EUA for use in children younger than 12 years of age or weighing less than 88 pounds (40 kg). There is limited information about the safety and effectiveness of using PAXLOVID in these patients.
Please see Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers and Fact Sheet for Patients, Parents, and Caregivers.
Important Safety Information
Significant Drug Interactions. PAXLOVID can interact with other medicines, causing severe or life-threatening side effects or death. Do not take PAXLOVID if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- alfuzosin
- amiodarone
- apalutamide
- carbamazepine
- colchicine
- dihydroergotamine
- dronedarone
- eletriptan
- enzalutamide
- eplerenone
- ergotamine
- finerenone
- flecainide
- flibanserin
- ivabradine
- lomitapide
- lovastatin
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
- lurasidone
- methylergonovine
- midazolam (oral)
- naloxegol
- phenobarbital
- phenytoin
- pimozide
- primidone
- propafenone
- quinidine
- ranolazine
- rifampin
- rifapentine
- St. John’s Wort (hypericum perforatum)
- sildenafil (Revatio®) for pulmonary arterial hypertension
- silodosin
- simvastatin
- tolvaptan
- triazolam
- ubrogepant
- voclosporin
These are not the only medicines that may cause serious or life-threatening side effects if taken with PAXLOVID. PAXLOVID may increase or decrease the levels of other medicines. It is very important to tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements, because additional laboratory tests or changes in the dose of your other medicines may be necessary during treatment with PAXLOVID. Your healthcare professional may also tell you about specific symptoms to watch out for that may indicate that you need to stop or decrease the dose of some of your other medicines. Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare professional.
Before taking PAXLOVID, tell your healthcare professional about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have kidney or liver problems, including hepatitis.
- have Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1) infection. PAXLOVID may lead to some
HIV-1 medicines not working as well in the future. - are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, breastfeeding, or plan to breastfeed. PAXLOVID can pass into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare professional if you are taking combined hormonal contraceptive (birth control). PAXLOVID may affect how your birth control works. People who can become pregnant should use another or an alternative effective form of birth control.
PAXLOVID may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Allergic reactions, including severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis). Do not take PAXLOVID if you are allergic to nirmatrelvir, ritonavir, or any of the ingredients in PAXLOVID. Stop taking PAXLOVID and call your healthcare professional right away if you get any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- skin rash, hives, blisters, or peeling skin
- painful sores or ulcers in the mouth, nose, throat, or genital area
- trouble swallowing or breathing
- swelling of the mouth, lips, tongue, or face
- hoarseness
- throat tightness
-
Liver problems. Tell your healthcare professional right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms of liver problems during treatment with PAXLOVID:
- loss of appetite
- yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes
- dark-colored urine
- pale-colored stools
- itchy skin
- stomach-area (abdominal) pain
The most common side effects of PAXLOVID include: altered sense of taste (such as metallic, bitter taste) and diarrhea.
Other possible side effects include:
- headache
- abdominal pain
- vomiting
- high blood pressure
- nausea
- feeling generally unwell
These are not all of the possible side effects of PAXLOVID. For more information, ask your healthcare professional or pharmacist.
There is limited experience treating pregnant women or breastfeeding mothers with PAXLOVID. For a mother and unborn baby, the benefit of taking PAXLOVID may be greater than the risk from the treatment. It is recommended that you use effective barrier contraception or do not have sexual activity while taking PAXLOVID. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, discuss your options and specific situation with your healthcare professional.
Take PAXLOVID exactly as your healthcare professional tells you. If you take too much PAXLOVID, call your healthcare professional or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. If you are taking a ritonavir- or cobicistat-containing medicine to treat hepatitis C or HIV-1 infection, you should continue to take your medicine as prescribed.
Talk to your healthcare professional if you do not feel better or if you feel worse after 5 days.
Contact your healthcare professional if you have any side effects that bother you or do not go away. Report side effects or problems with the appearance or packaging of PAXLOVID to FDA MedWatch at www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-10881-800-FDA-1088, or you can report side effects to Pfizer Inc. at www.pfizersafetyreporting.com, by fax at 1-866-635-83371-866-635-8337, or by calling 1-800-438-19851-800-438-1985.
Please see Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers and Fact Sheet for Patients, Parents, and Caregivers.
AUTHORIZED USE
The FDA has authorized the emergency use of PAXLOVID for the treatment of mild-to-moderate
PAXLOVID is not FDA-approved or available under EUA for use in children younger than 12 years of age or weighing less than 88 pounds (40 kg). There is limited information about the safety and effectiveness of using PAXLOVID in these patients.
You are now leaving this website.
By clicking this link, you will be redirected to a website that is neither owned nor controlled by Pfizer. Pfizer is not responsible for the content or services of this site.
You are now leaving paxlovidinformation.com
The information provided at paxlovidhcp.com is intended only for healthcare professionals in the United States.
